Network and connectivity requirements for Oracle environments
General port allocation
The Delphix Engine makes use of the following network ports regardless of the type of database platform:
General outbound from the Delphix engine port allocation
Protocol | Port numbers | Use |
|---|---|---|
TCP | 25 | Connection to a local SMTP server for sending email |
TCP/UDP | 53 | Connections to local DNS servers |
UDP | 123 | Connection to an NTP server |
UDP | 162 | Sending SNMP TRAP messages to an SNMP Manager |
TCP | 443 | HTTPS connections from the Delphix Engine to the Delphix Support upload server |
TCP/UDP | 636 | Secure connections to an LDAP server |
TCP | 8415 | Connections to a Delphix replication target. See Configuring Replication |
TCP | 50001 | Connections to source and target environments for network performance tests. |
General inbound to the Delphix engine port allocation
Protocol | Port number | Use |
|---|---|---|
TCP | 22 | SSH connections to the Delphix Engine |
TCP | 80 | HTTP connections to the Delphix GUI |
UDP | 161 | Messages from an SNMP Manager to the Delphix Engine |
TCP | 443 | HTTPS connections to the Delphix Management Application |
TCP | 8415 | Delphix Session Protocol connections from all DSP-based network services including Replication, SnapSync for Oracle, V2P, and the Delphix Connector. |
TCP | 50001 | Connections from source and target environments for network performance tests via the Delphix CLI. |
Firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS)
Production databases on source environments (for dSources) are often separated from the non-production environment by firewalls. Firewalls can add milliseconds to the latency between servers. Accordingly, for best performance, there should be no firewalls between the Delphix Engine and the virtual database (VDB) target environments. If the Delphix Engine is separated from a source environment by a firewall, the firewall must be configured to permit network connections between the Delphix Engine and the source environments for the application protocols (ports) listed above.
Intrusion detection systems (IDSs) should also be made permissive to the Delphix Engine deployment. IDSs should be made aware of the anticipated high volumes of data transfer between dSources and the Delphix Engine.
SSHD configuration
Both source and target Unix environments are required to have sshd running and configured such that the Delphix Engine can connect over ssh.
The Delphix platform expects to maintain long-running, highly performant ssh connections with remote Unix environments. The following sshd configuration entries can interfere with these ssh connections and are therefore disallowed:
Disallowed |
|---|
|
|
Network and connectivity requirements for Oracle
IP connections must exist between the Delphix Engine and the source and target environments.
For source environments, Delphix Engine uses an SSH connection to each source host, an HTTP connection from each source environment to Delphix Engine, and a DSP connection to the Delphix Engine. The Delphix Engine uses SQLNet connections to the DBMS on the source environment.
For target environments, Delphix uses an SSH connection to each target environment and an NFS connection to Delphix Engine. Delphix Engine uses SQLNet connections to the virtual databases on the target environment.
scp Availability
The scp program must be available in the environment in order to add an environment.
Port allocation for Oracle environments
The following diagram describes the port allocations for Oracle environments. It illustrates the ports that we recommend to be open from Delphix to remote services, to the Delphix Engine, and to the Target Environments.
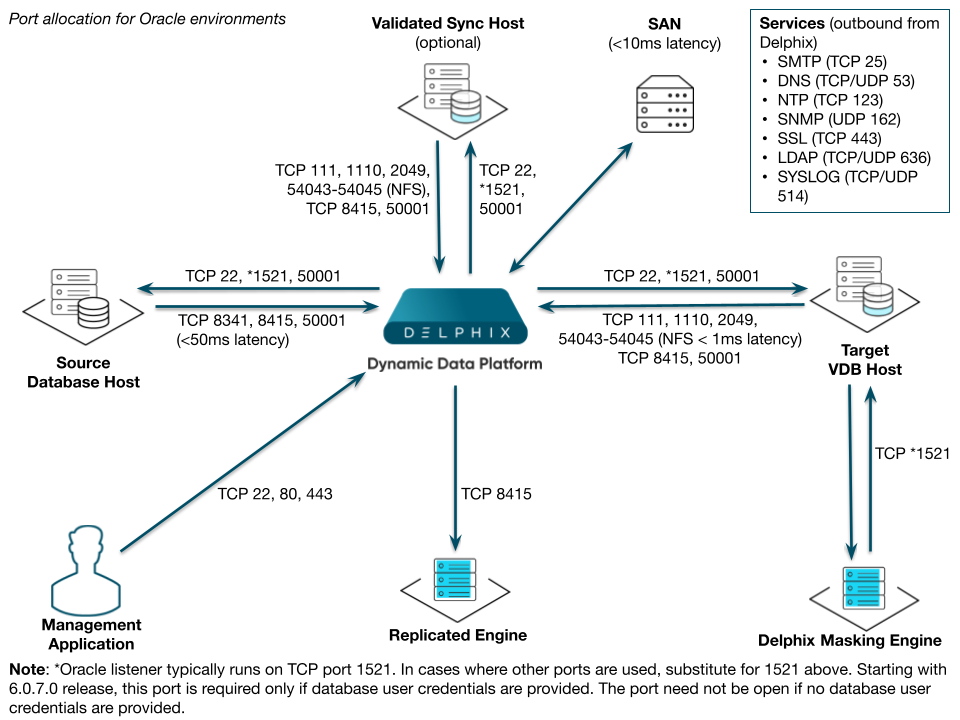
The Delphix Engine makes use of the following network ports for Oracle dSources and VDBs:
Outbound from the Delphix engine port allocation
Protocol | Port numbers | Use |
|---|---|---|
TCP | 22 | SSH connections to source and target environments |
TCP | xxx | Connections to the Oracle SQL*Net Listener on the source and target environments (typically port 1521) |
Inbound to the Delphix engine port allocation
Protocol | Port number | Use |
|---|---|---|
TCP/UDP | 111 | Remote Procedure Call (RPC) port mapper used for NFSv3 mounts Note: RPC calls in NFSv3 use additional fixed ports for supporting services (lockd, mountd and statd) seen below. |
TCP | 1110 | NFSv3 Server daemon status and NFS server daemon keep-alive (client info) |
TCP/UDP | 2049 | NFS Server daemon from VDB to the Delphix Engine (used for both NFSv3 and NFSv4) |
TCP | 8341 | Sending data from source to the Delphix Engine (for LogSync) |
TCP | 8415 | SnapSync control and data from source to the Delphix Engine V2P control and data from the target environment to the Delphix Engine. |
TCP | 54043 | NFSv3 mount daemon |
TCP | 54044 | NFSv3 stat daemon (lock state notification service) |
TCP | 54045 | NFSv3 lock daemon/manager |
UDP | 33434 - 33464 | Traceroute from source and target database servers to the Delphix Engine (optional) |
AppData port requirements
The use of AppData requires the following ports/protocols. Two important notes about these specifications:
The next release of the Delphix Engine will significantly augment the port/protocol utilization of AppData. The upcoming-only requirements have been marked with a *.
AppData V2P uses RSYNC to export to the target. RSYNC between the target and Delphix Engine is not required for general virtualization usage. The V2P-only requirements have been marked with a ^.
From source to Delphix engine | From Delphix engine to source | From target to Delphix engine | From Delphix engine to target |
|---|---|---|---|
RSYNC (TCP Port 873) | RSYNC (TCP Port 873) | DSP (Default TCP Port 8415) | DSP (Default TCP Port 8415) |
DSP (Default TCP Port 8415) | SSH (TCP Port 22) | NFS | SSH (TCP Port 22) |
*NFS | DSP (Default TCP Port 8415) | ^RSYNC (TCP Port 873) | ^RSYNC (TCP Port 873) |
