Working with multiple container owners
Delphix Self-Service administrators can designate multiple users as owners of a single data container. These users all share access to the same data container, meaning actions taken by one user will impact all users on the same data container.
For example, if user A activates branch X, user B will also see branch X as the active branch. This ability for one user action to impact another user on the same containers creates new concerns for users sharing the same container.
As a result, more processes should be put into place to coordinate usage between users. Each team is different, but some effective strategies include:
Designating a person to perform certain data operations.
Saving your work with a bookmark or creating/working on a personal branch.
Being aware of who is using your data container/data before performing operations.
Locking a container to prevent others from performing any operations on it.
How many owners should a container ideally be shared between?
There is no technical limit built into the software, but it is best if a team of 5-10 users shares a single data container. In most cases, having fewer owners minimizes overhead and conflicting usage. One owner per container provides maximum productivity and minimal overhead, so this feature should only be used if your infrastructure or processes require that multiple users share a container. Additionally, Jet Stream-only users currently cannot see other users with whom they share the container.
How should users handle potentially disruptive operations?
If one user performs an operation on a data container, it will affect the other owners of that container. Additionally, each user has permission to perform the same operations on the data container; currently there are no fine-granularity permissions that limit the operations a user can perform. All operations are potentially disruptive, but the level of disruption varies by operation. If any of the following operations are performed at the same time, the second operation will fail due to a conflict when processing the job.
Conflicting operations
Refresh
Restore
Reset
Enable/Disable
Create Branch
Activate Branch
Delete Branch
Create Bookmark
Delete Bookmark
If user A performs a destructive operation while user B is "using" the data container, the operation will destroy user B’s current state. Currently, the interface does not provide insight into whether the data container is in use by another user.
Destructive operations
Refresh
Restore
Reset
Enable/Disable
Create Branch
Activate Branch
Deleting objects
All owners can delete any bookmarks or branches in the container, regardless of who created them.
Coordinating users
Opportunity for disruption increases as more owners are sharing a single container. Sharing a container works best when users can communicate with each other, for example, they are part of the same team and working with the container at different times.
Additionally, these disruptions can be avoided when Delphix Self-Service users lock their containers to prevent other users from performing operations on them. Users cannot see the other users with whom they share the container. However, if a user locks a container, only that user will be able to use the container; it will appear disabled to others.
What operations could disrupt others using a container?
Potentially disruptive operations include:
Refresh
Switching active branches
Deleting bookmarks
Creating Branches
Un-sharing bookmarks
Restore
Reset
Staring/ stopping your container
Where can I see which user has performed what operation?
You can see which user has performed which action in the History tab of the Data Operations screen.
Be aware that operation counts in the template view are currently tabulated based on the container, not the user performing the operation.
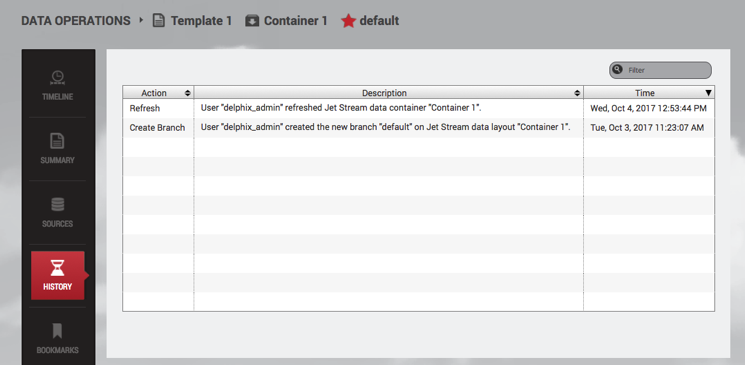
DATA OPERATIONS → HISTORY
Where can I see which containers are unlocked/locked?
Unlocked containers can be viewed by typing unlocked in the search filter.
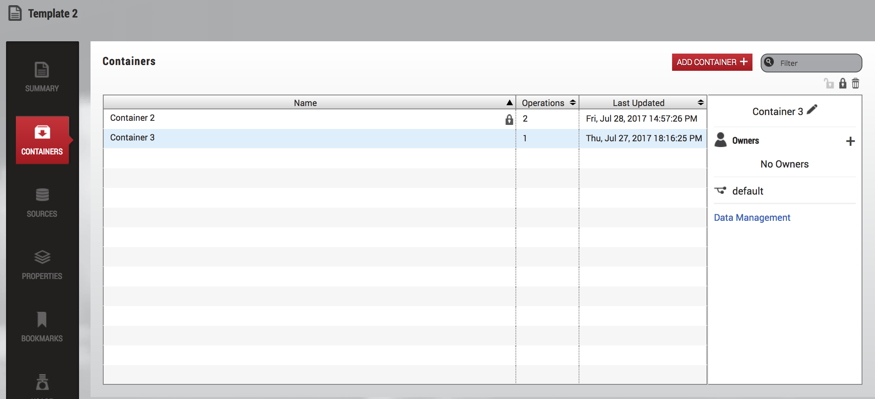
You can view locked containers by typing locked in the search filter. To find containers locked by a specific user, type locked by {username} in the search filter.